Short list for setting a hatchery

The first question you need to put on the table is :
-
What kind of fish species you want to reproduce ?
-
Or are they crustaceans, such as lobsters (homards), spiny lobsters (langoustes), nephrops (langoustines), crabs (crabes), crawfishes (écrevisses), shrimps (crevettes Penaeidae), prawns (chevrettes) or an unknown type ?
-
Or will you work with bivalves (mollusks) ?
The second question that comes to my mind is for what purpose exactly ?
-
Is it for a small or big ornamental aquarium ?
-
Or is it for food production with raceways or ponds ?
Then, you need to consider the following :
-
From where suitable breeders should come from ? This is particularly important for mass production (versus individual spawning).
-
What are the requirements for this particular species ? (Such as the limits for temperature, salinity, etc.)
-
Do you have basic notions in genetics, selection and fertilization ? (This is most important to discard or improve key fishes)
-
Use appropriate facilities to maintain and use these breeders (such as a net above their ponds for protection against predators like birds, otters, thieves, etc.).
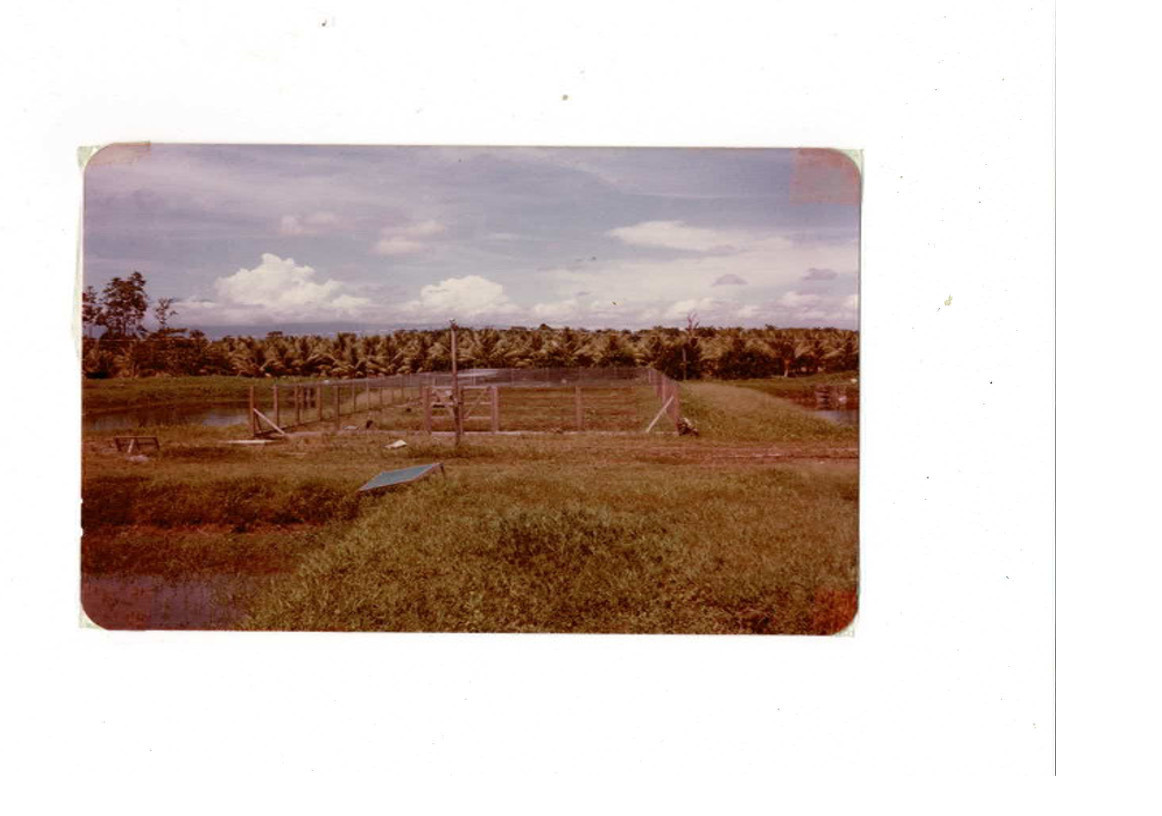


-
Algal culture production should be seriously considered, as it is the primary food for larvae : choose different cell sizes with nutional specificities, such as Chaetoceros, Isochrysis, Chorella, Skeletonema, Dunalliela, Pavlova, Tetraselmis, Thalassiosira, etc.
-
Do consider also eggs counting/evaluation : use a haemocytometer, a binocular, a microscope or an optical/coulter counter.
-
If you consider fishes, you will have to deal with :
° Natural or/and artificial spawning techniques ;
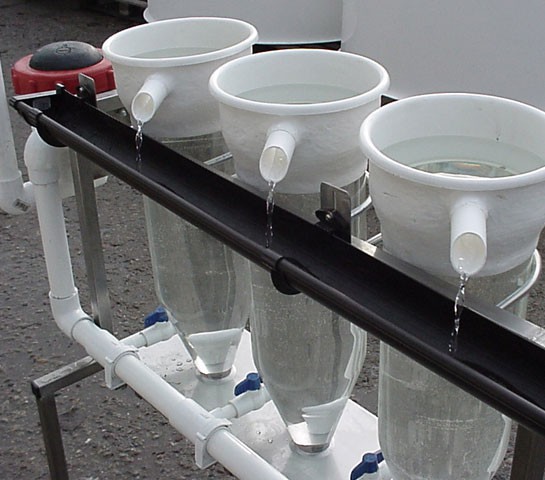
° Use of Kakabans or Zoug bottles for eggs ;
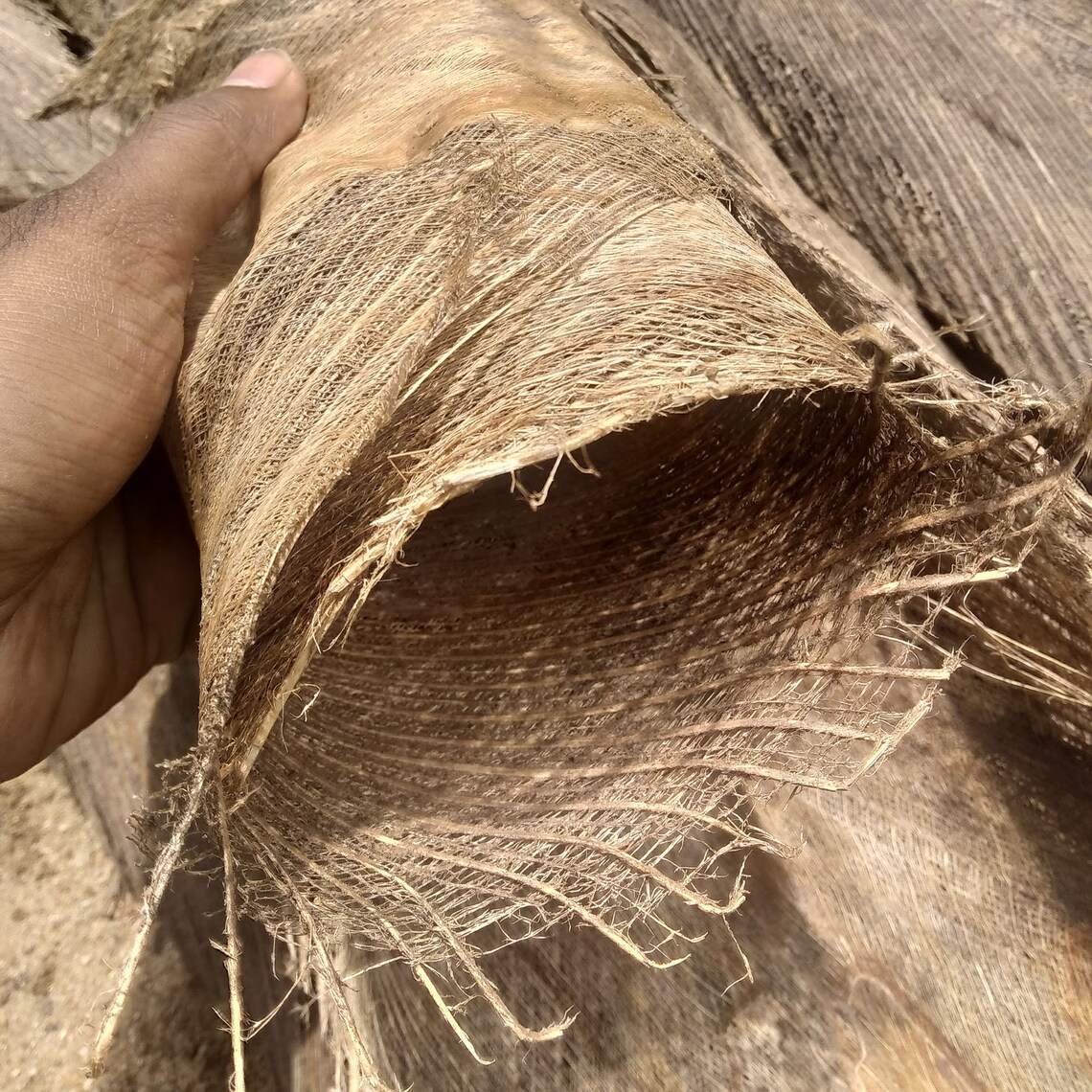
Kakabans - See details at the end of the article (1)
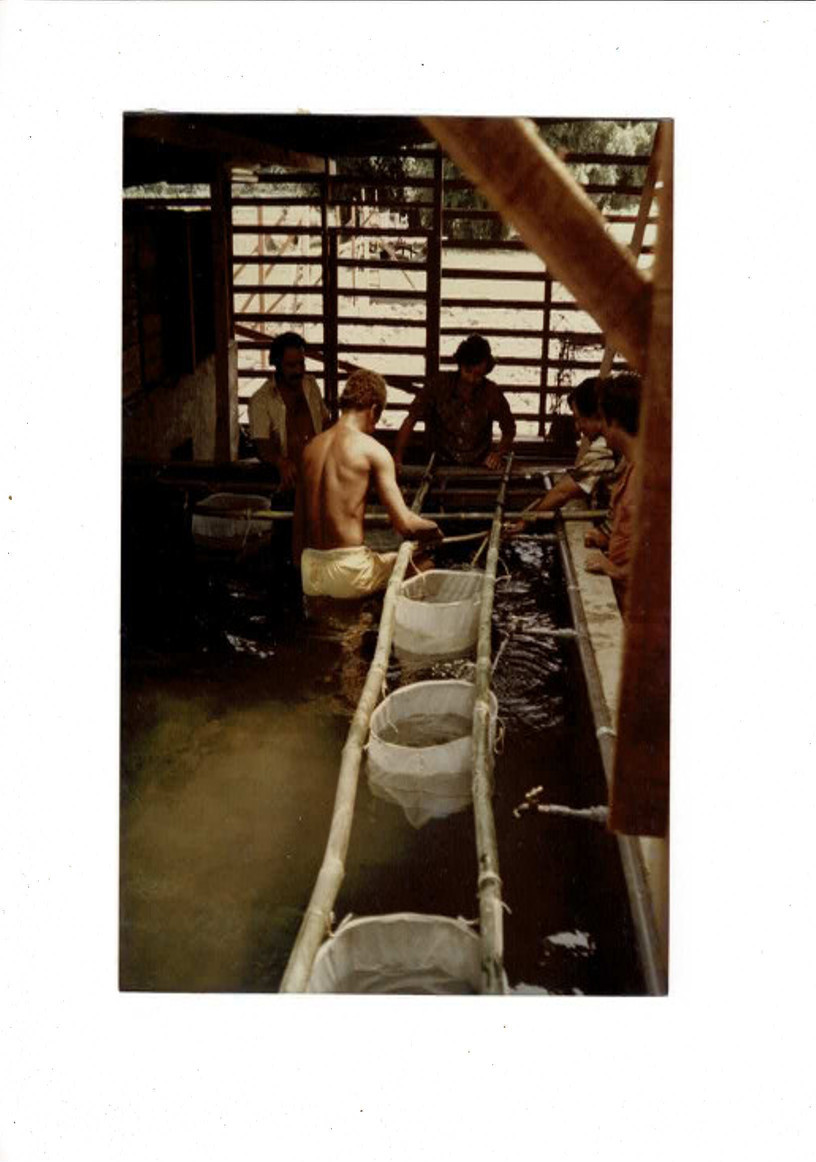

Just above, artisanal Zoug bottles; industrial ones at the top of the article
° Special profile tanks for larval rearing ;
° Circular tanks for juvenile development ;

° After these first steps, ornamental and edible animals need growing facilities ;
° Are they omnivorous, herbivorous or carnivorous ?
° According to their profile, use meals/flours, sinking/floating pellets, flakes or natural food (zooplankton, insects, mulberry leaves, etc.).
-
If you consider crustaceans, you will have to look at :
° Special care about male/female breeders and light management by setting day/night lengths ;
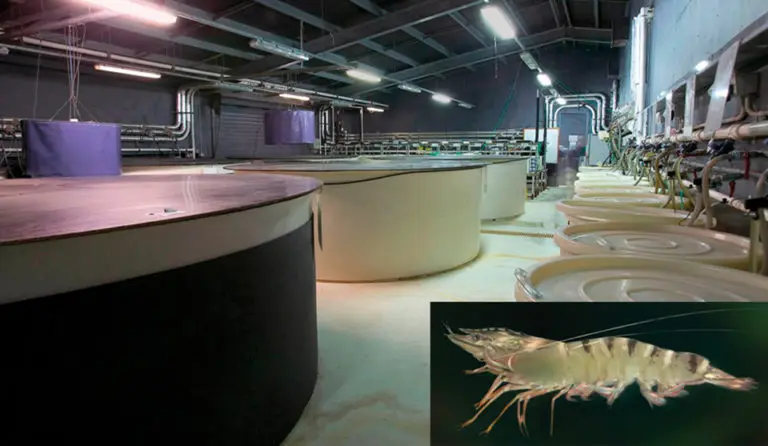

° Eggs fertilization ;
° Larval development in relation with nutritional requirements for each species (use of special feed, such as micro-algae, Daphna, Rotifers, Artemia, fed Artemia, mussels, squids, etc.) ;
° Juveniles use frequently indoor circular tanks ;
° Later, commercial growth takes place within intensive raceways or outdoor ponds, using pellets (for high densities) or natural food (for extensive production).
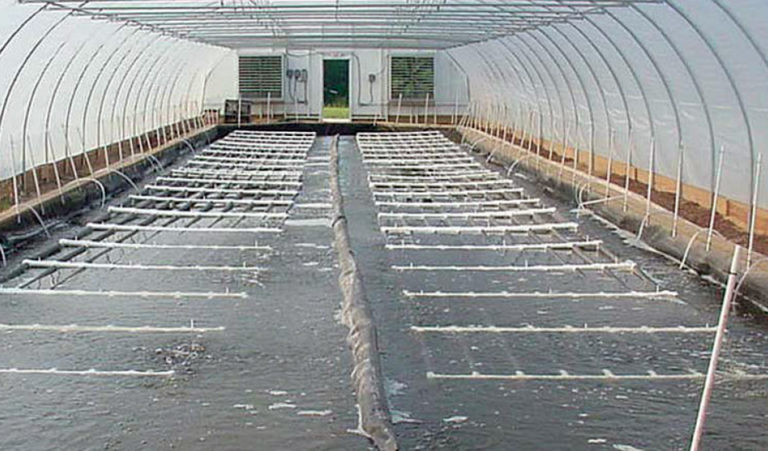


-
If you consider mollusks (for instance, oysters), care should be paid to :
° Eggs manipulation (oysters are one time male, the other female) ;
° Ciliated trochophore stage ;
° Straight-hinge stage ;
° Umbo stage ;
° Eyed stage ;
° Pediveliger stage (spat), produced with good phytoplankton.
In some cases, sieves are needed for harvesting and selection.
Water will have to be filtered, using sand, gravel, diatomea (backwashing) and industrial micro-filters.
Information will give suitable feed, as it is related to mouth size and requirements in nutrition for each stage.
Water quality needs to be understood for controlling temperature, salinity, pH, nitrites, nitrates and other key elements.
Larvae survival (i.e. mortality reduction) should be mastered to reach minimal production.
Diseases need to be prevented and/or controlled. This means identifying parasites, bacteria, virus and looking at unappropriated environment. Quick decision needs to be taken for any suitable treatment if recovery is still possible.
So, you see that equipment and good actions are fundamental for nursery management.
Studies and experiences can greatly help you.
Planning is essential for success !
__________________________
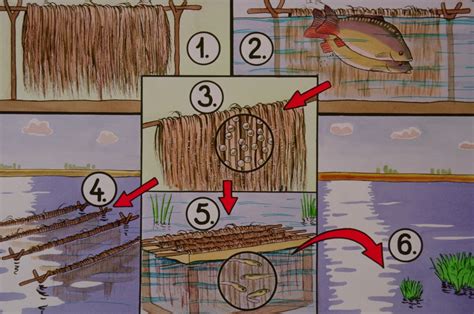
(1) This can be built from disinfected coconut trunk coir, as shown by the following pictures:


